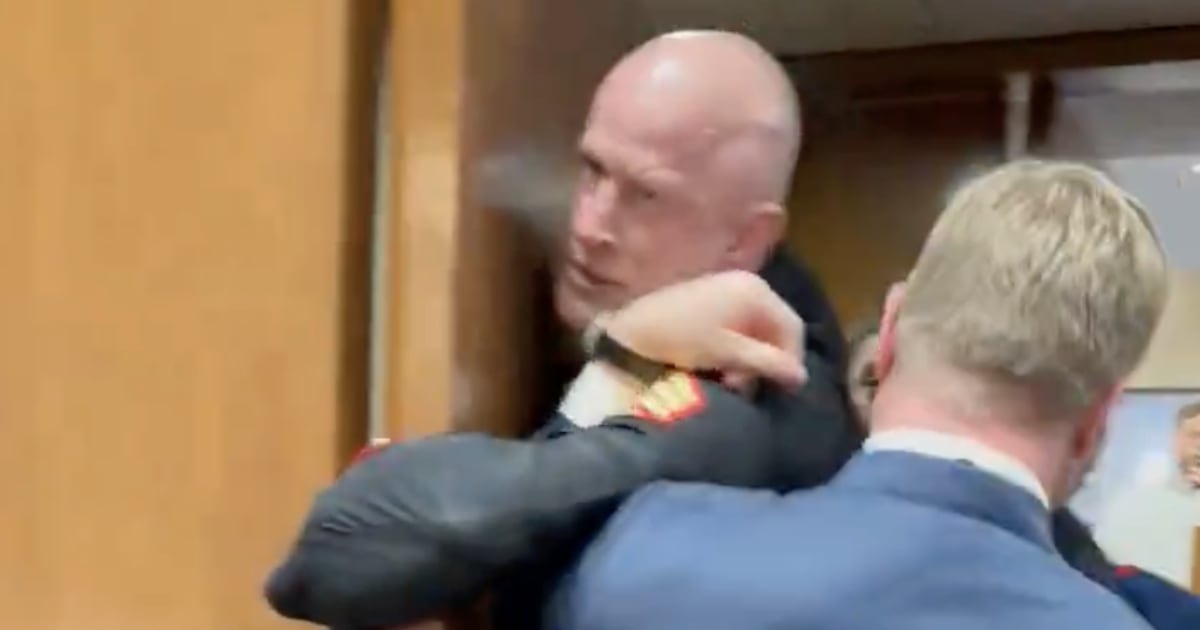
Bureaucratic restrictions and public-relations concerns from the Army and top Trump administration Pentagon appointees unreasonably restrained the D.C. National Guard from responding to the Jan. 6 Capitol insurrection, its commander testified to the Senate in a dramatic Wednesday session.
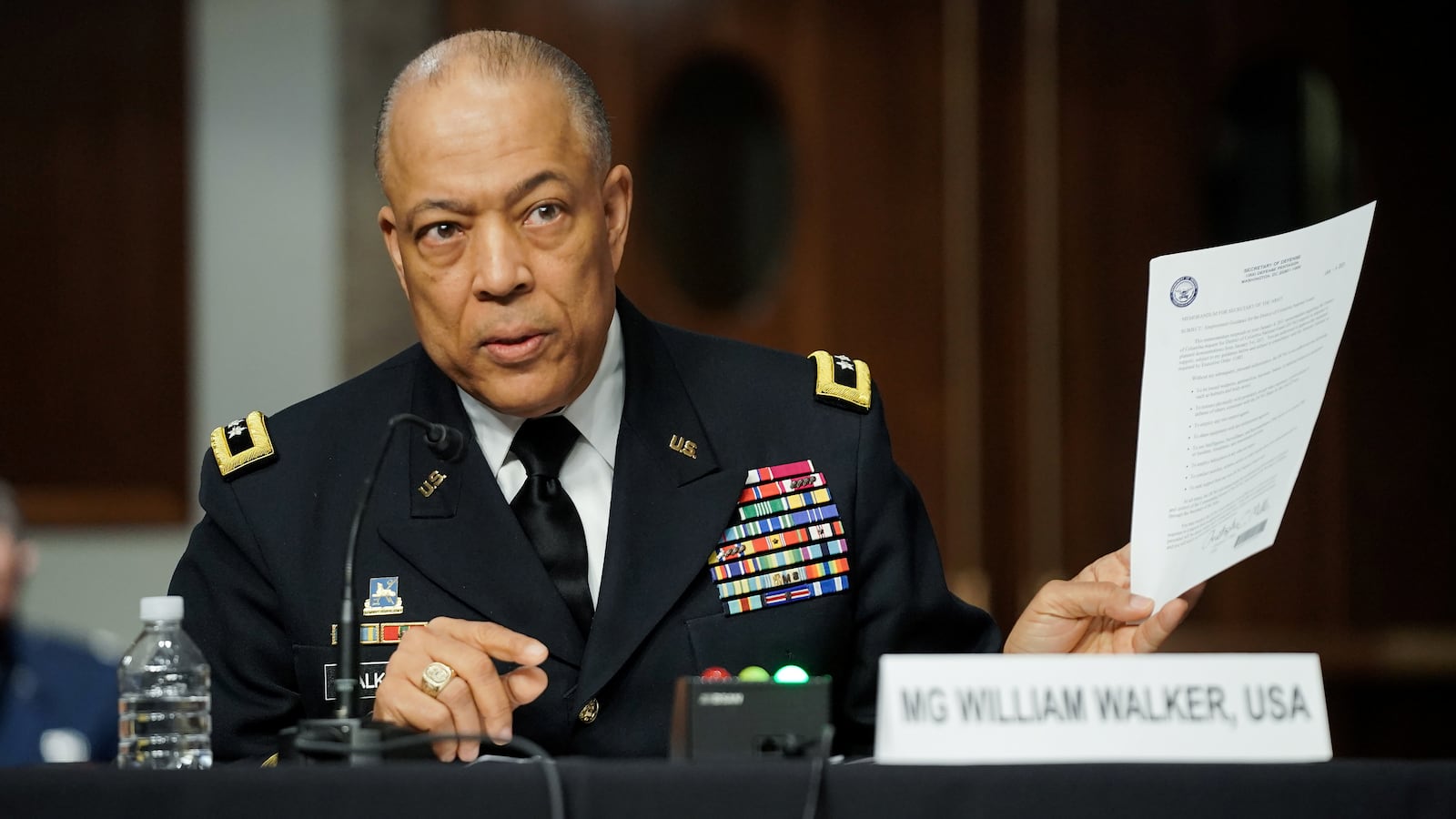
The Guard commander, Major General William Walker, described receiving a “frantic” phone call from the then-head of the Capitol Police, Steven Sund, shortly before 2 p.m., as the breach was underway.
Yet because of the restrictions from Acting Defense Secretary Chris Miller, Secretary of the Army Ryan McCarthy, and the “best military advice” of senior Army officers, Walker and his 155 Guardsmen could not respond to the scene of the insurrection for another three hours and 19 minutes—restrictions Walker pointedly noted were not placed upon him during the summer’s Black Lives Matter protests in Washington, D.C.
Had Walker been able to deploy to the Capitol “immediately,” as he testified he wanted, around 2 p.m.—a process he said took less than 20 minutes—“that number could have made a difference,” Walker said. “We could have helped extend the perimeter and pushed back the crowd.”
It was perhaps the most intense moment thus far in a series of Senate hearings on Jan. 6 that have prompted dueling claims of irresponsibility, recriminations that have focused overwhelmingly on security and intelligence failures, rather than the politicians who spread the inciting lie that the Democrats stole the presidential election and hailed the violent protest called for by President Donald Trump.
Army and Pentagon officials have heard this critique from Walker in the press and pushed back on it. Yet it was clear at the hearing that even senior Republican senators considered the Pentagon’s restrictions on the D.C. National Guard unacceptable.
Walker described pre-insurrection letters from McCarthy, relaying instructions from Miller—whom Trump installed atop the Pentagon shortly after losing the election—that withheld from Walker the issuance of “weapons, ammunition, batons, ballistic protection equipment, to include body armor.” He did not have preapproval to mobilize a quick-reaction force of 40 Guardsmen and found it “unusual” to be denied a typical commanders’ authority to protect his own forces.
As well, Walker described an instruction that afternoon from McCarthy to provide a “concept of operations” for the Guard before getting approval to shift from backing up the D.C. police and relieving beleaguered Capitol Police officers. “In 19 years, I never had that before happen,” Walker told senators. In several instances that day, Walker acted on his own initiative to muster the quick-reaction force at the D.C. Armory and get his Guardsmen protective gear, ahead of the belated approval to deploy to the Capitol.
Neither Miller nor McCarthy testified. Instead, a senior Pentagon civilian, Robert Salesses, was left to effectively testify that Walker was wrong.
Walker testified that two Army three-star generals, Charles Flynn and Walter Piatt, told him on Jan. 6 afternoon phone calls that they advised against sending the Guard to the Capitol because it was a poor “optics” and “could incite the crowd.” Salesses stoically said that Piatt, who is not in the chain of command, told him he never “used the word ‘optics,’” which represents the second revision in Piatt’s story, as the Army general recently acknowledged he may have indeed used that word.
Walker shot back: “There were people in the room with me on that call that heard what they heard.”
But Salesses’ broader point was that the restrictions Miller placed on Walker were political. “There was a lot of things that happened in the spring the department was criticized for,” Salesses said, referring to the Pentagon’s use of the National Guard to suppress the Black Lives Matter protests in Washington.
Yet Salesses, questioned by Republican senators, could not explain all the Pentagon restrictions on the National Guard.
The National Guard was on the streets of D.C. on Jan. 6 to support the D.C. police, in an unarmed and unarmored fashion, at 30 city traffic-control points and six Metro stations. Walker said he had to seek approval from the Pentagon to accompany the police in moving a traffic point over by a single block. The quick-reaction force, stationed initially at Joint Base Andrews just outside the district, was “not [designed] to respond to the events of the Capitol,” Salesses pleaded. “I don’t know if that’s true,” Sen. Rob Portman (R-OH) replied, quickly prompting Walker’s agreement.
Salesses also had to concede that over a half-hour passed between his account of Miller finally authorizing the Guard deployment, at 4:32 p.m., and notifying Walker of that decision at 5:08 p.m. Asked what accounted for that delay by an incredulous Sen. Roy Blunt (R-MO), Salesses said only, “Senator, it’s an issue.”
“That’s a significant problem for the future,” Blunt said.