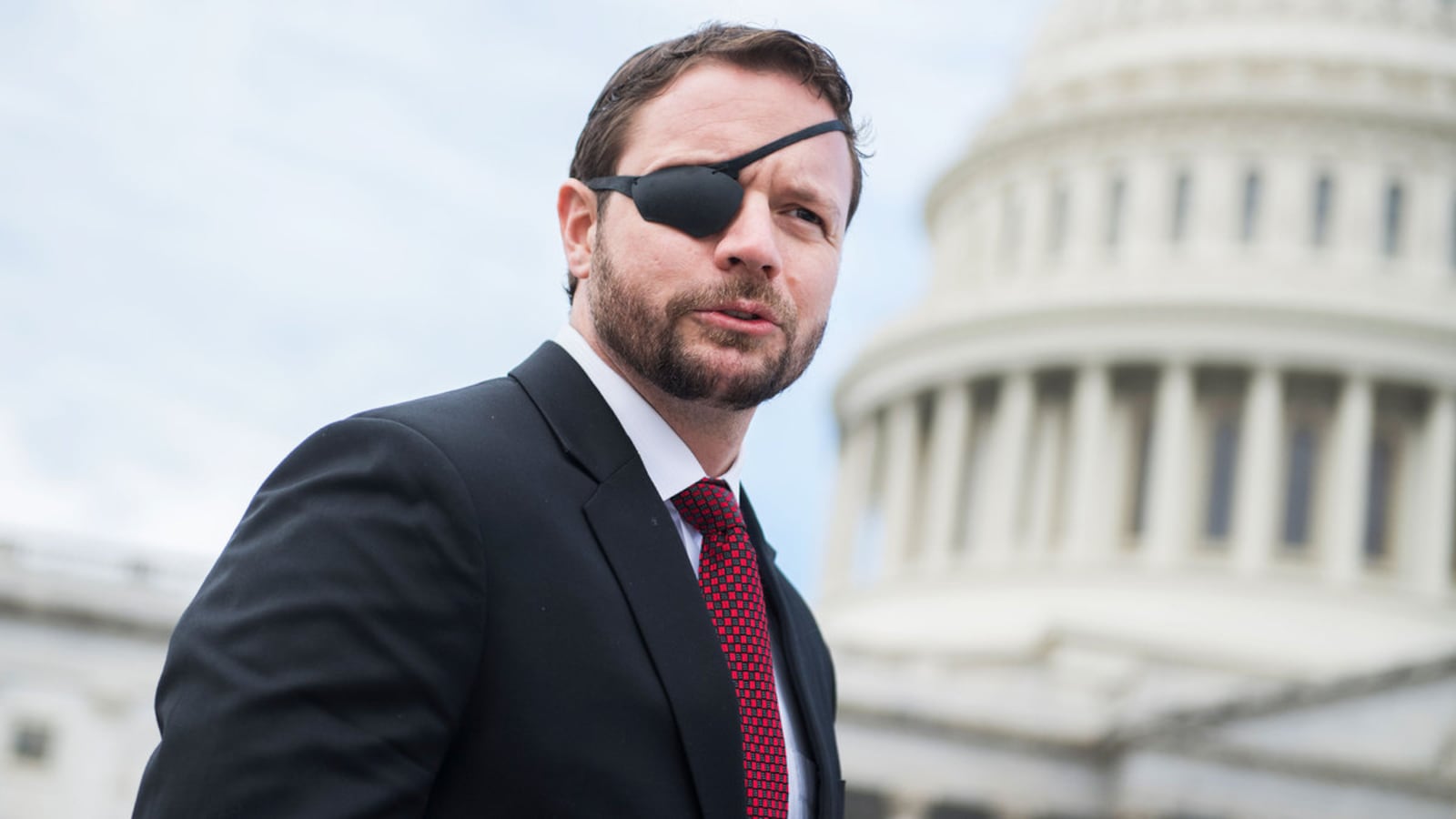
Rep. Dan Crenshaw (R-TX) did not buy or sell any stocks in his first 13 months as a congressman. That changed in March 2020, when he made half a dozen buys as the largest economic relief package in history was written and debated.
Five of those purchases came in the three days between March 25 and 27, as the Senate and House voted on the CARES Act and former President Trump signed it into law. Crenshaw, who supported the bill, did not initially disclose the transactions, in violation of the STOCK Act, a law that requires members of Congress to tell the public when they engage in securities trades. Months later he amended his records to reflect the purchases.
The trades, which are listed only in a range of values, add up to a maximum of $90,000, and do not compare in size or volume to the kinds of headline-grabbing transactions executed ahead of the pandemic by Sens. Kelly Loeffler and David Perdue. They only appeared in December, when Crenshaw amended his annual report, originally submitted in August.
“You’re referencing financial disclosures that use a range to report stock purchases, and you’re choosing the upper end of the range to come up with that [$90,000] figure,” Justin Discigil, Crenshaw’s communications director, told the Daily Beast in an email. “The real number is around $30,000 at most,” Discigil said, and “in no way were his purchases unethical or related to official business.”
The timing, however, along with Crenshaw’s own trading history and connections to the industry, raises questions about why he made the purchases and failed, twice, to disclose them.
“Members of Congress should not be actively trading securities in the middle of a crisis. It shows that when the market crashes, that person is thinking about themselves and using the volatility to their own advantage,” said Ben Edwards, a securities law expert and professor at the William S. Boyd School of Law at the University of Las Vegas Nevada. “We all have a limited amount of attention, and if you’ve got [an] eye on your stock portfolio, then you’re not giving that crisis or the American people the full attention they demand.”
Crenshaw, elected in 2018, had never traded individual stocks in office until that crisis struck, according to public records. Then, when global markets crashed on March 12, Crenshaw bought between $1,001 and $15,000 in Amazon. Two weeks later, while Congress voted on the CARES Act, Crenshaw bought stocks valued at the same price range in Southwest, Boeing, energy infrastructure manfacturer SPX, and Kinder Morgan, a Texas-based company specializing in pipeline construction. He also bought into an index fund tied to the performance of the S&P 500.
While it’s unclear why Crenshaw did not initially disclose the transactions, they came as an increasing number of high-profile lawmakers were getting snared in an insider-trading scandal. Except for the Amazon purchase, all of Crenshaw’s transactions came a week after ProPublica reported that Sen. Richard Burr (R-NC) had sold up to $1.72 million on the heels of private coronavirus briefings. On March 20, The Daily Beast reported that Loeffler and her husband had sold off seven figures worth of stock following her first confidential briefings on the pandemic. Scrutiny soon fell on trades executed by Sens. David Perdue (R-GA), Jim Inhofe (R-OK), Dianne Feinstein (D-CA) and John Hoeven (R-ND), spurring investigations by the Justice Department, the Senate Ethics Committee and the Securities and Exchange Commission. None of the lawmakers faced criminal charges. Perdue and Loeffler lost their re-election bids to Democratic challengers Jon Ossoff and Rev. Raphael Warnock in runoff elections this January.
In response to the scandal, the Campaign Legal Center analyzed all congressional stock trades made between Feb. 2 and April 8, finding that a dozen senators made a combined 127 transactions in the timeframe, and 37 House members made at least 1,358 transactions.
Crenshaw’s name did not make it into those media reports, however, because he hadn’t disclosed his purchases. The STOCK Act, a 2012 law intended to deter federal elected officials from trading on inside knowledge, requires congress to post all transactions within 45 days. Not only did Crenshaw fail to disclose the transactions at the time, he didn’t include them in his annual disclosure, filed in August. And while that filing shows that Crenshaw holds the new assets, the form also requires members to list the transactions, including the dates, which Crenshaw left blank. They only appeared when the Lone Star Republican filed an amended annual report in December.
Crenshaw’s spokesperson told The Daily Beast that the Harvard alum and former Navy SEAL had filed that amendment “to fix clerical issues in his report like making sure dates were correct.”
At the time of the transactions, congress was scrambling to put together the CARES Act, a monumental emergency relief package that cost more than $2 trillion, and which Crenshaw supported. The Republican-led Senate approved the bill on March 25, the day Crenshaw bought stock in SPX and the S&P 500 fund. The package passed the House the next day, when Crenshaw scooped up Southwest and Kinder Morgan, and was signed into law by Trump on March 27, the day that Crenshaw acquired his stake Boeing.
At the time, Crenshaw sat on the House committees for Budget and Homeland Security. Boeing in particular lobbied heavily, and successfully, for a piece of the CARES Act, asking at first for $60 billion and later hoping to receive a $17 billion slice that lawmakers set aside for “businesses critical to maintaining national security.” The nonpartisan Institute on Tax and Economic Policy said at the time that it was “generally understood that the bill’s authors want much, if not all, of this $17 billion to go to a single company: Boeing.” But in late April, the manufacturer passed on the deal, opting instead to raise $25 billion in private investment thanks to moves that the Federal Reserve made independently of the CARES Act. The day that Crenshaw bought Boeing, markets snapped their brief positive burst, and the company led the boards that day in losses. His investment has now grown more than 38%. Boeing’s employee PAC gave $3,000 to Crenshaw’s 2020 campaign.
All of Crenshaw’s purchases have shown returns, with the biggest yields from Boeing, Amazon and Southwest Airlines. Amazon bounced up from about $1,820 a share on March 12 to $2,979 today, and Southwest Airlines rose from around $41 to a little over $60.
“It’s not hard to see that airlines would be among the hardest-hit stocks in a global pandemic that restricted air travel,” Edwards said. “So the short-term is that they’re going to get hammered, but in the long term, the sky is going to be busy again.” That calculation includes the likelihood that the federal government would pitch in to keep the industry aloft, and in mid-April the airlines got their $25 billion bailout.
Edwards said that while the limited available information makes it impossible to know why Crenshaw and other officials make specific trades, new reforms introduced in response to the trading scandal would make such transactions impossible.
“Some of the proposals for limiting stock purchases would really cut back on activity like this. For instance, Senator Warren’s plan would prohibit buying and selling individual stocks, and just allowing members to track markets through index funds,” he said. “Another proposal is to require lawmakers to disclose their trading plans in advance, which executives of publicly traded companies already do. That would reduce the likelihood or suspicion that they’re using private information or their own legislative powers to their advantage.”
Kedric Payne, senior director of ethics at the Campaign Legal Center, told The Daily Beast in November that lawmakers in the public’s trust shouldn’t risk even the appearance of having a personal financial stake in their government work.
"It is nearly impossible to make decisions affecting an industry and then receive a personal financial benefit without appearing to have a conflict of interest," Payne said. "Even if officials rely on financial advisors to make trading decisions on their behalf, the perception of conflicts of interest remains, because the public does not know if there are winks and nods prompting the trades."
Last week, Business Insider reported that Rep. Tom Malinowski (D-NJ), an advocate for transparency, had failed to disclose dozens of stock transactions over the course of 2020. Malinowski, who like Perdue — but unlike Crenshaw — claims that a third-party financial adviser independently executes his trades, said that his time in the barrell sharpened his appetite for reform.
“This does reinforce my view that members of Congress should not be invested in the stock market or, if they are, they should not have any visibility into the stocks they own,” Malinowski later told NJ.com. “Inevitably, even if the decisions are made by an investment firm with no input from the member of Congress, there can be this perception of influence because what we do in Congress affects every aspect of the economy.”
Crenshaw doesn’t own many individual stocks, currently. Beyond the trades in March, he only holds shares in Starbucks, Alphabet — Google’s parent company — and a small stake in Schlumberger, a global oilfield services provider primarily based in Europe, with a branch in Houston. The energy-dependent metropolis also hosts Kinder Morgan, but the offices of both companies are located just outside the lines of Crenshaw’s gerrymandered district.
The trades intersect with Crenshaw’s government work, specifically in energy. The oil and gas industry contributed a total $453,247 to his 2020 re-election efforts, and was his largest industry patron in terms of PAC donations. And while this may not have posed a direct conflict of interest last year, that may no longer be the case: On Jan. 21, House Republican leadership took Crenshaw off of his Homeland Security and Budget committee assignments and moved him to the Committee on Energy and Commerce.